In April, 13.4% of all Open Unemployment Fund members received earnings-related allowance from the fund, while the number of recipients remained at the March level. Compared to last year, however, the number of recipients has increased significantly, 30.5% from last April. This April, earnings-related allowance costs reached 48.1 million euros, an increase of 32.1% from April 2023.
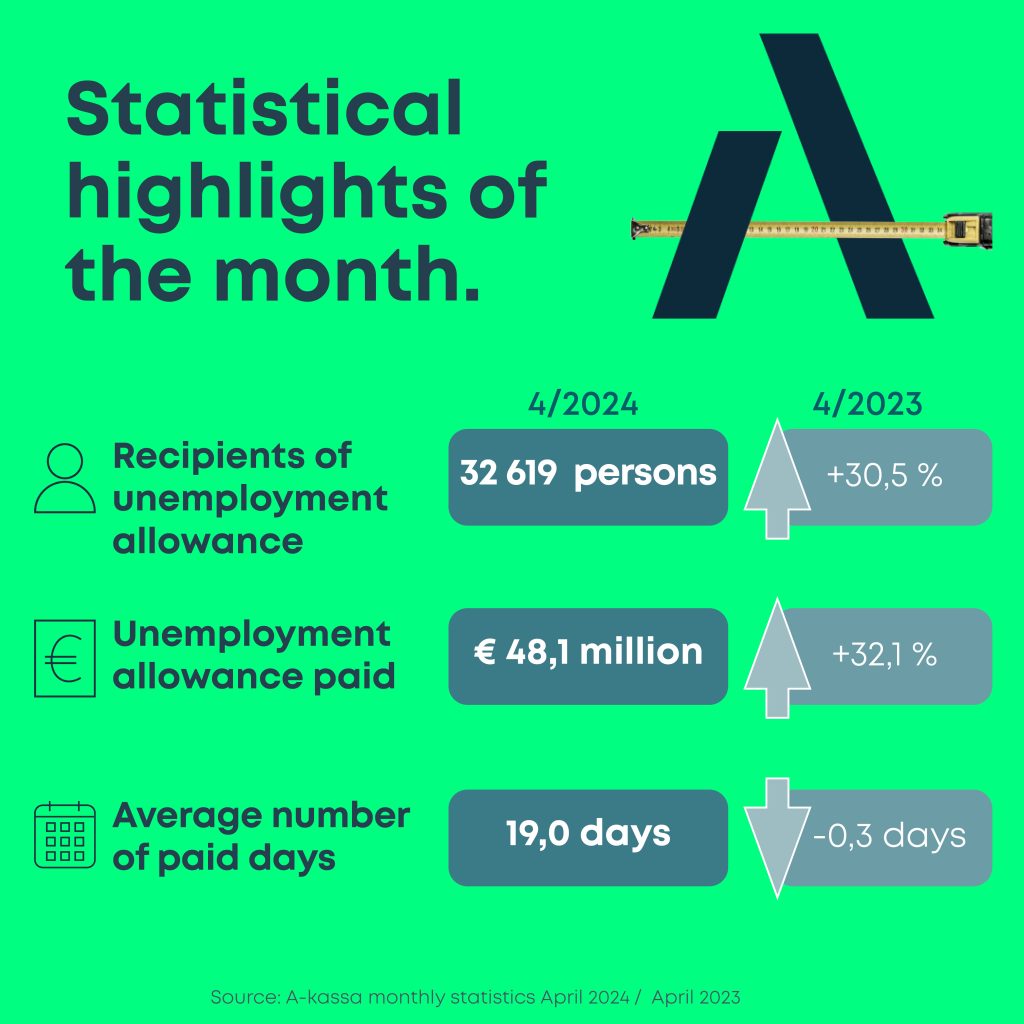
In April, a total of 32,619 members received earnings-related allowance from the Open Unemployment Fund, a slight increase from March. Compared to April 2023, the number of recipients was up 30.5%, a significant increase as the number was 24,986 last year. Unlike the previous year, when the number of recipients decreased from March to July, the figure has remained constantly high throughout the beginning of the year. The growth rate has, however, slowed down a bit.
43.7% of earnings-related allowance recipients were laid off, an increase of 1.2 percentage points from March. Therefore, the share of lay-off period daily allowance recipients remains high. The share of laid-off persons has remained high since last autumn, exceeding 42% throughout the early part of 2024. Meanwhile, the share of adjusted daily allowance recipients has remained at 13%.
Earnings-related allowance costs up
The clear downward trend in earnings-related allowance costs from January through March was cut short in April, with the costs going up 3.4 million from March. The costs reached 48.1 million euros in April, representing an increase of 32.1% compared to April 2023. Last year, paid-out earnings-related allowance costs grew moderately until March, took a downward turn in April and continued to decrease until July. Suffice to say, the numbers paint a different picture this year.
Downward trend in number of payout days ends
The downward trend from January through March in number of payout days came to an end in April when the number of days increased to 19, up 1.1 days from March. While we saw similar development in the number of payout days in 2023, the upswing peaked in May.
In April, A-kassa received a total of 40,420 earnings-related allowance applications, over 500 more than in March and 29% more than in April of last year. Most of the applications, 61.8%, were follow-up applications. The share of first-time applications increased 0.9 percentage points from March, standing now at 8.8%. Applications for adjusted allowance made up 29.4% of all applications.
Even with the large amount of applications received, A-kassa continued to improve its processing time in April. First-time applications had an average processing time of 8.6 days in April, down 2.7 days from March. And with a processing time of 5.1 days, applications for adjusted allowance were processed slightly faster than in March.
Lots of positive feedback for our customer service
Our phone service received a total of 7,870 calls in April, with an average response time of 2:25 minutes. Based on our phone service feedback survey, 73% of respondents were highly satisfied and 19% quite satisfied with the service.
We received 4,918 messages via our eService in April, down 6% from March. Our chat service hosted a total of 1,131 discussions in April, with an average queuing time of 39 seconds and an average discussion length of 10:43 minutes. Based on our chat service feedback survey, 73% of respondents were highly satisfied and 16% quite satisfied with A-kassa’s service.
Monthly statistical summaries are available at the A-kassa website